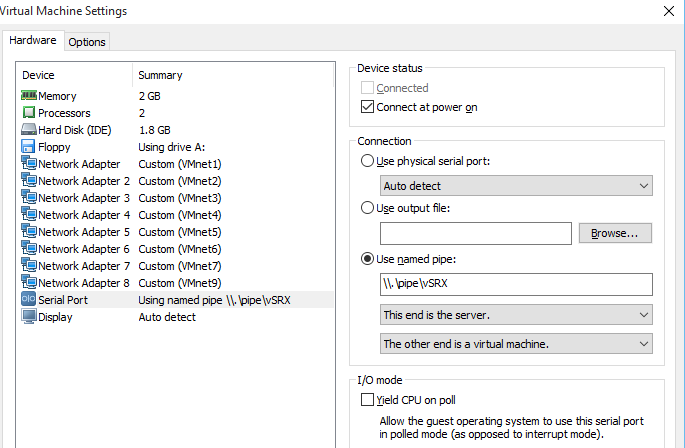
Buat anda yang tertarik belajar product security juniper, dalam hal ini adalah SRX. juniper menyediakan tools nya yang dikenal dengan juniper firefly atau juniper vSRX. related juniper secuirty anda bisa membacanya disini. oke anda harus mendownload juniper firefly di junipervsrx (dengan filename;junos-vsrx-12.1X47-D20.7-domestic.ova). Setelah vsrx dam vmware ada di local disk anda. Anda perlu install vmware nya terlebih dahulu setelah itu anda tinggal open file vsrx yang anda download sebulmnya. Silahkan ikuti detail step nya pada tulisan bagaimana memulai belajar juniper. Jika anda mengikuti step nya, minimal coba anda buat kebutuhan interface vsrx seperti tampilan berikut 🙂
Category: Juniper
[Junos Security] Pengenalan Juniper Security
Hallo pagi semuanya 🙂
Mumpung lagi fresh, masih pagi dan pas banget ini adalah materi awal terkait juniper firewall. Tulisan ini adalah diperuntukkan buat siapa ja yang ingin mengenal product juniper firewall. Yup, tentu anda tau ya pasti apa itu firewall? tembok api bukan? betul, gk tau kenapa perangkat security diistilahkan sbg firewall, klo dalam sejarah2 dunia banyak bangunan atau tembok raksasa yang sengaja dibangun untuk mempertahankan diri dari musuh hehe, sebut saja tembok besar cina, tembok berlin, dan lain-lain. mungkin itu kali ya. Oke jadi product security, semua vendor mengistilahkan sebagai firewall. Nah firewall ini tentu setiap product memiliki feature yang berbeda-beda, tapi fitur2 dasar pasti ada. Klo sebelumnya kita banyak dengar istilah stateless firewall, statefull firewall, traditional firewall, yang baru sekrang istilahnya lagi next generation firewall (NGFW). Sedikit saja mengenai istilah tersebut klo stateless firewall itu kayak access-list di cisco (cisco lagi haha), eh klo di juniper ada juga lah istilahnya firewall filter itu sama dengan cisco, jadi intinya gmn klo stateless? intinya adalah perangkat (biasanya router) hanya menforward paket berdasarkan paket header nya, atau routing table, stateless ini tidak men-track sessionnya itu secara dua arah. misal session saat paket itu berangkat dan saat paket balik lagi. nah klo firewall saat ini sudah statefull, jadi dia akan terus men-track session bolak-baliknya. oke lanjut dulu ya untuk detailnya nanti ane tulisin dibawah hehe. Terus klo traditional firewall bisa kita compare dengan NGFW, jadi traditional firewall memang sudah statefull, tapi content yang dia cek hanya dari IP sampai layer transport dalam hal ini prtokol2 yang termasuk UDP atau TCP, sedangkan NGFW itu sudah mampu melihat atau mengecek atau mengontrol sampe layer aplikasi, baik itu aplikasinya, content, user dan bahkan informasi-informasi yang ada di dalamnya.
Lanjut ya, jadi untuk memahami lebih detail apa yang kita bicarakan diatas, coba kita compare perbedaan router dan firewall.
Bagaimana Memulai Belajar Juniper?
As request by owner routecloud 🙂 ada yang butuh referensi bagaimana memulai belajar juniper? Jadi kita harus mulai dari mana? dan apa ja yang dibutuhkan? that’s your questions maybe ya? hehe..
Kita mulai dari hal2 yang teoritis dulu, jadi kalo semua perangkat network dan security juniper dari low sampai high end itu menggunakan satu operating system namanya JUNOS. Junos ini based on nya adalah Unix FreeBSD yang mana adalah salah satu OS open source. Jadi bila anda manage router kecil sampai yang besar sekalipun, anda bisa melakukannya dengan cara yang sama, berbeda dengan vendor cisco yang perangknya menggunakan berbagai macam operating system.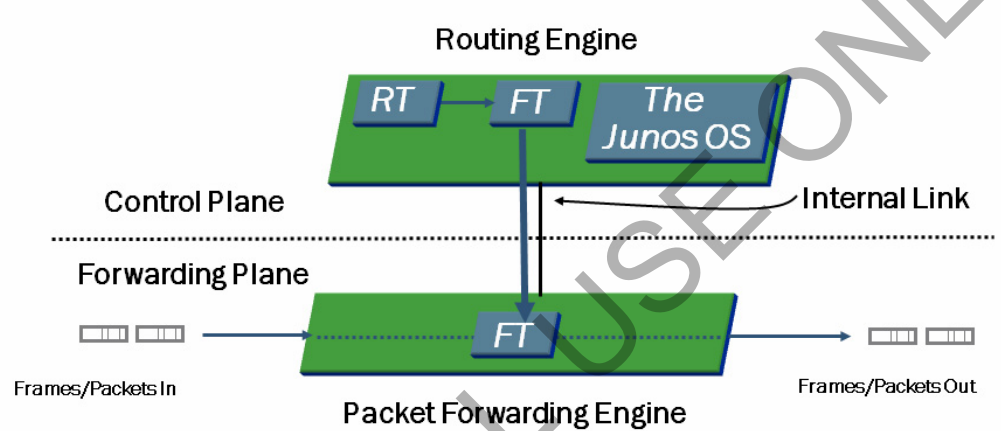 Read More
Read More
[Junos Routing] Konfigurasi Internal BGP Peer
hello everybody, ini adalah tulisan pertama ane di tahun 2016 hehe, pada kesempatan ini mau memulai tulisan tentang protokol bgp. Oke sekilas mengenai bgp, bgp adalah routing protokol antar AS (autonomous system). BGP biasanya digunakan pada jaringan skala besar, seperti jaringan enterprise yang besar yang menggunakan lebih dari satu koneksi atau multiple koneksi ke ISP, bgp juga digunakan dalam jaringan service provider.
Kemudian bgp ini mendukung dua jenis pertukaran informasi routing. Pertukaran informasi routing antar AS atau beda AS itu dikenal sebagai external bgp (EBGP) atau disebut juga EBGP Session. Sedangkan pertukaran routing dalam AS yang sama dikenal dengan internal bgp (IBGP) atau IBGP session.
Sekilas mengenai bgp cukup ya, silahkan lanjut …
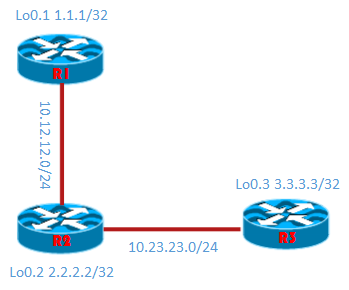 sesuai dengan judul tulisan ini, kita akan membahas bagaimana mengkonfigurasi internal bgp atau IBGP, hal yang perlu anda ketahui mengenai bgp adalah anda tidak bisa mengkonfigurasi seperti model routing protokol yang lain yang bisa mempelajari routingnya secara dinamis, namum bgp anda harus mengenalkan secara manual, yang nanti akan anda lihat, kemudian bgp juga dbangun dari routing protokol IGP seperti ospf, isis, atau eigrp pada cisco, jadi untuk memahami bgp, anda perlu memahami protokol IGP terlebih dahulu. Lalu bagaimana dengan IBGP, untuk model konfigurasinya kita perlu mengenalkan alamat local router ke dalam bgp, dan router tersebut perlu peering ke router yang mana saja, sebagai contoh R3 pengen komunikasi ke R2 dan R1. sebagai R3 perlu mengenalkan alamatnya yang nanti dikenal juga ke R2 dan R1, R3 juga harus kenal dan mengenalkan alamat R2 dan R1 ke dalam bgp R3, bisa dipahami ya bahasanya hehe..( nanti akan paham klo ngikutin konfignya 🙂 )
sesuai dengan judul tulisan ini, kita akan membahas bagaimana mengkonfigurasi internal bgp atau IBGP, hal yang perlu anda ketahui mengenai bgp adalah anda tidak bisa mengkonfigurasi seperti model routing protokol yang lain yang bisa mempelajari routingnya secara dinamis, namum bgp anda harus mengenalkan secara manual, yang nanti akan anda lihat, kemudian bgp juga dbangun dari routing protokol IGP seperti ospf, isis, atau eigrp pada cisco, jadi untuk memahami bgp, anda perlu memahami protokol IGP terlebih dahulu. Lalu bagaimana dengan IBGP, untuk model konfigurasinya kita perlu mengenalkan alamat local router ke dalam bgp, dan router tersebut perlu peering ke router yang mana saja, sebagai contoh R3 pengen komunikasi ke R2 dan R1. sebagai R3 perlu mengenalkan alamatnya yang nanti dikenal juga ke R2 dan R1, R3 juga harus kenal dan mengenalkan alamat R2 dan R1 ke dalam bgp R3, bisa dipahami ya bahasanya hehe..( nanti akan paham klo ngikutin konfignya 🙂 )
Oke mari kita lanjutkan ke tahap konfigurasinya Read More
[Junos Routing] Troubleshooting Tools untuk OSPF
Baik, sbelumnya anda perlu cek dlu tulisan seblumnya disini, ini kita akan membhas hal yang lebih spesifik yaitu bagaimana tshoot network ospf. Untuk tshoot ospf ada 2 cara yaitu dengan protokol traceoptions, sama mengguakan command show. Untuk traceoptions ini sama dengan fitur debug pada pada cisco 🙂 Oke dsni pertama saya akan bhas sedkit mengenai protokol traceoptions ini, pertama anda perlu melakukan configurasi terlebih dahulu untuk bisa mengaktikannya. config ini dilakukan pada R5 pada topology seblumnya.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
root@JuniperX# show protocols ospf { traceoptions { file trace-ospf-r5; flag error detail; flag event; } |
Anda bisa mengaktifkan berbgai fitur traceoptions dengan under command flag seperti berikut:
[Junos Routing] OSPF Inter Area, Stub Area dan NSSA Area
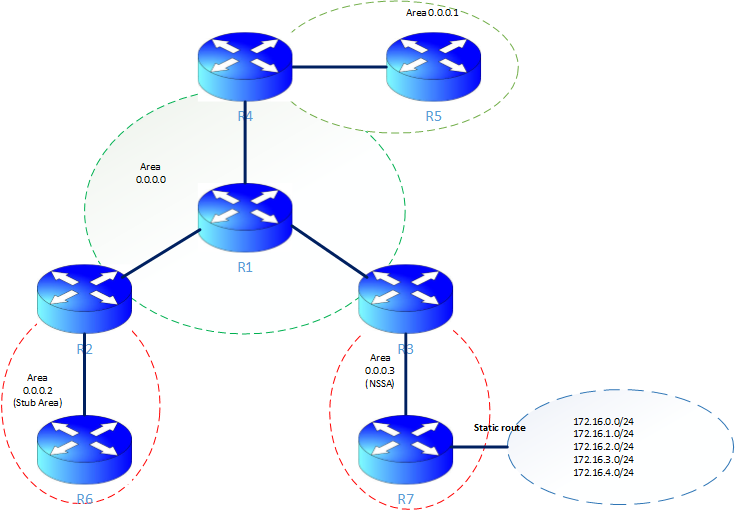
Hello everbody :), ini menyambung tulisan2 sebelumnya, kali ini ane menfokuskan bagaimana ospf bekerja pada area yang berbeda, atau ospf bekerja pada stub areas atau not-so-stubby areas atau dikenal dengan ospf nssa. biar lebih ngerti mari kita lihat gambar berikut:
sesuai dengan judul tulisan ini, mau tak bahas sedikit, jadi ada yang namananya backbone area, jadi ini adalah area 0, nah untuk area selain area 0 harus koneksi dengan area 0 minimal salah satu routernya. nah kemdian komunikasi antara area 0 dengan area 1 dan lain-lain dikenal dengan inter area. terus ada lagi yang namanay stub area ini adalah area dimana tidak area lagi yang lain dibawahnya atau istilahnya tidak lagi domain network yang lain dibawahnya. untuk NSSA area itu mirip dengan stub area, namun ini lebih fleksibel, kenapa? karean setalh nssa area masih boleh ada area lain, atau domain network yang lain misal static route atau dynamic route.
Okeh sudah ada gambaran ya kira2? 🙂 mari kita lihat step konfignya.
Step 01 : konfigurasi interface ke semua router.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
R1 set interfaces em1 unit 12 vlan-id 12 set interfaces em1 unit 12 family inet address 10.12.12.1/24 set interfaces em1 unit 13 vlan-id 13 set interfaces em1 unit 13 family inet address 10.13.13.1/24 set interfaces em1 unit 14 vlan-id 14 set interfaces em1 unit 14 family inet address 10.14.14.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 1.1.1.1/32 R2 set interfaces em2 unit 12 vlan-id 12 set interfaces em2 unit 12 family inet address 10.12.12.2/24 set interfaces em2 unit 26 vlan-id 26 set interfaces em2 unit 26 family inet address 10.26.26.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 2.2.2.2/32 R3 set interfaces em3 unit 13 vlan-id 13 set interfaces em3 unit 13 family inet address 10.13.13.3/24 set interfaces em3 unit 37 vlan-id 37 set interfaces em3 unit 37 family inet address 10.37.37.3/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 3.3.3.3/32 R4 set interfaces em4 unit 14 vlan-id 14 set interfaces em4 unit 14 family inet address 10.14.14.4/24 set interfaces em4 unit 45 vlan-id 45 set interfaces em4 unit 45 family inet address 10.45.45.4/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 4 family inet address 4.4.4.4/24 R5 set interfaces em3 unit 13 vlan-id 13 set interfaces em3 unit 13 family inet address 10.13.13.3/24 set interfaces em3 unit 37 vlan-id 37 set interfaces em3 unit 37 family inet address 10.37.37.3/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 3.3.3.3/32 R6 set interfaces em6 unit 26 vlan-id 26 set interfaces em6 unit 26 family inet address 10.26.26.6/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 6 family inet address 6.6.6.6/32 R7 set interfaces em7 unit 37 vlan-id 37 set interfaces em7 unit 37 family inet address 10.37.37.7/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 7 family inet address 7.7.7.7/32 |
Step 02: Konfig router-id
Pada lab ini router-id, kita tentukan sendiri yakni menggunakan interface loopback.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
R1 set routing-options router-id 1.1.1.1 R2 set routing-options router-id 2.2.2.2 R3 set routing-options router-id 3.3.3.3 R4 set routing-options router-id 4.4.4.4 R5 set routing-options router-id 5.5.5.5 R6 set routing-options router-id 6.6.6.6 R7 set routing-options router-id 7.7.7.7 R5 set routing-options router-id 5.5.5.5 |
Step 03: Konfig protocol ospf area 0 dan inter-area
Supaya lebih mudah memahami, sebaiknya perhatikan lagi gambar diatas, karea ane juga udah bikinin, jadi sayang klo gk dilihat 🙂 , oke jadi R1 itu berada di area 0.
|
1 2 3 4 |
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface em1.12 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface em1.13 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface em1.14 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 |
Selanjutnya, mari kita lihat config R4 dan R5 berikut.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
R4 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface em4.14 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.4 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface em4.45 R5 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface em5.45 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface lo0.5 |
Jadi ospf area 0 pada R1 misalnya sekarang sudah bisa ngobrol dengan area 1 pada R5. Oke kita laanjutkan saja, dengan config ospf untuk interface yang koneksi langsung dengan R1 pada R2 dan R3.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
R2 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface em2.12 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.2 R3 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.3 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface em3.13 |
Mari kita lihat hasilnya pada R5, dengan melakukan show route,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
root@JuniperX# run show route 1.1.1.1 logical-system r5 inet.0: 21 destinations, 21 routes (21 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 1.1.1.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:51:54, metric 2 > to 10.45.45.4 via em5.45 [edit] root@JuniperX# run show route 2.2.2.2 logical-system r5 inet.0: 21 destinations, 21 routes (21 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 2.2.2.2/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:51:57, metric 3 > to 10.45.45.4 via em5.45 [edit] root@JuniperX# run show route 3.3.3.3 logical-system r5 inet.0: 21 destinations, 21 routes (21 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 3.3.3.3/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:52:06, metric 3 > to 10.45.45.4 via em5.45 |
Bila anda cek disisi R1, R2, R3, route yang menuju 5.5.5.5/32 di R5 sudah ditemukan juga :). Berikut penampakannya.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
root@JuniperX# run show route 5.5.5.5 logical-system r3 inet.0: 22 destinations, 22 routes (22 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 5.5.5.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:57:35, metric 3 > to 10.13.13.1 via em3.13 |
So, ospf inter-area sudah clear ya..:), klo sudah lanjut ke step berikutnya,
Step04 : Konfigurasi ospf stub are.
Baik, untuk area 0.0.0.2 atau area 2 pada R2 dan R6 merupakan stub area, nah mari kita lihat selengkpnya.
|
1 2 3 |
R2 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 stub no-summaries set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 interface em2.26 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
R6 set protocols ospf export static2ospf set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 stub default-metric 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 stub summaries set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 interface em6.26 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 interface lo0.6 set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.26.26.2 set policy-options policy-statement static2ospf term 1 from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static2ospf term 1 then accept |
untuk config stub area, under area 0.0.0.2 pilih stub baik pada R2 maupun R6, jadi keduanya harus dikenalin sebgai ospf area stub. kemdian under command stub ada pilihan summaris dan no-summaries. Ini bergantung keputusan anda, dilihat dari R2 bila anda pakai summaries maka semua LSA type pada area 0 pada R2 akan disynkronkan dengan database area 2, sederhananya adalah semua informasi routing yang diterima pada area 0 akan diterima juga oleh R2 dan R6 sebagai area 2 (stub area). nah klo sperti itu otomatis kurang efisien dari sisi resource, dan kurang aman dari sisi security, karea semua informasi routing akan diterima oleh R6 tentunya. Oleh karena itu disni menggunakan opsi no-summaries, klo di R6 itu opsional, R2 yang menentukan.
Nah R6 biar bisa ngobrol dengan ospf area lain, maka anda cukup tambahin default route, R2 sebagai gateway nya. jangan lupa redistribute static policy nya di export ke ospf area 2 biar dikenal sebgai ospf. Oke mari kita lihat hasilnya.
berikut show ospf database pada R2, bisa juga anda coba rubah dengan opsi no-summaries lalu cek lagi ospf databasenya.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
root@JuniperX# run show ospf database logical-system r2 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.0 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 0x800000bf 1190 0x22 0xd77b 72 Router *2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x8000008d 1762 0x22 0x3005 48 Router 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x80000078 1732 0x22 0xa88d 48 Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x8000007f 523 0x22 0xf111 60 Network *10.12.12.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000036 1190 0x22 0xc309 32 Network 10.13.13.3 3.3.3.3 0x8000003b 1462 0x22 0x9c20 32 Network 10.14.14.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000046 689 0x22 0x693d 32 Summary 5.5.5.5 4.4.4.4 0x80000008 1190 0x22 0x26ea 28 Summary *6.6.6.6 2.2.2.2 0x80000008 2335 0x22 0x34e0 28 Summary 7.7.7.7 3.3.3.3 0x80000009 100 0x22 0xe526 28 Summary *10.26.26.0 2.2.2.2 0x8000004d 2908 0x22 0xe3c5 28 Summary 10.37.37.0 3.3.3.3 0x8000002f 373 0x22 0x4a9 28 Summary 10.45.45.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000045 2852 0x22 0x182 28 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.2 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router *2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000042 583 0x20 0x4717 36 Router 6.6.6.6 6.6.6.6 0x8000005a 1195 0x20 0x7882 48 Network 10.26.26.6 6.6.6.6 0x80000016 1195 0x20 0xf8b1 32 |
keliatan kan, jadi pada area 2 hanya ada LSA type 1 dan 2 :), mari kita cek pada R6
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
root@JuniperX# run show ospf database logical-system r6 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.2 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000042 1198 0x20 0x4717 36 Router *6.6.6.6 6.6.6.6 0x8000005a 1808 0x20 0x7882 48 Network *10.26.26.6 6.6.6.6 0x80000016 1808 0x20 0xf8b1 32 |
woww, lah klo kayak gini gimana bisa ngobrol dengan R1 dan yang lainnnya, tenang mari coba kita lihat dengan show route.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
root@JuniperX# run show route logical-system r6 inet.0: 5 destinations, 5 routes (5 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 0.0.0.0/0 *[Static/5] 01:21:56 > to 10.26.26.2 via em6.26 6.6.6.6/32 *[Direct/0] 05:00:04 > via lo0.6 10.26.26.0/24 *[Direct/0] 01:21:56 > via em6.26 10.26.26.6/32 *[Local/0] 01:21:56 Local via em6.26 224.0.0.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 05:00:04, metric 1 MultiRecv |
biar jelas, mari kita coba trace ke R5
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
root@JuniperX# run traceroute 5.5.5.5 logical-system r6 traceroute to 5.5.5.5 (5.5.5.5), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.26.26.2 (10.26.26.2) 0.361 ms 0.166 ms 0.104 ms 2 10.12.12.1 (10.12.12.1) 0.213 ms 0.242 ms 0.200 ms 3 10.14.14.4 (10.14.14.4) 0.300 ms 0.317 ms 0.320 ms 4 5.5.5.5 (5.5.5.5) 0.423 ms 0.423 ms 0.384 ms |
sipp, jalan ya :), keuntungannya pada R6, jika networknya besar, anda tidak butuh router dnegan kapasitas table routing yang besar bukan? suatu langkah penghematan tentunya heheh (sampe sini lanjut sholat dulu)
Step 05: OSPF NSSA
Dari gambar tentu anda jg sudah paham ya, klo gtu mari kita lanjutkan saja, perhatikan config R3 dan R7 berikut sesuai dngan gambar
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
R3 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa default-lsa default-metric 10 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa default-lsa metric-type 1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa default-lsa type-7 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa no-summaries set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 interface em3.37 R7 set protocols ospf export static2ospf set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 interface em7.37 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 interface lo0.7 set policy-options policy-statement static2ospf term 1 from protocol static set policy-options policy-statement static2ospf term 1 then accept |
mari kita lihat satu persatu, pada R3, untuk config nssa under ospf area anda bsa set dnegan command nssa untuk menset area tersebut sebaga nssa area, lalu opsi no-summaries sperti yang sudah dbhas sbelumnya. bila sudah secara otomatis R7 tidak akan menerima semua update routing dari router area lain. akan tetapi bila lakukan test ping, network anda akan tetap bisa mencapai R7, tapi dari R7 tidak bisa, maka dperlukan satu langkah lagi dengan melakukan redistribute default route 0.0.0.0/0 ke ospf dengan cara menambahkan command nssa default-lsa default-metric 10 metric-type 1 type-7. mari kita lihat hasilnya.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
root@JuniperX# run show ospf database logical-system r3 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.0 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 0x800000c1 1606 0x22 0xd37d 72 Router 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x8000008f 2207 0x22 0x2c07 48 Router *3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x8000007a 2151 0x22 0xa48f 48 Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000081 939 0x22 0xed13 60 Network 10.12.12.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000038 1608 0x22 0xbf0b 32 Network *10.13.13.3 3.3.3.3 0x8000003d 1878 0x22 0x9822 32 Network 10.14.14.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000048 1105 0x22 0x653f 32 Summary 5.5.5.5 4.4.4.4 0x8000000a 1605 0x22 0x22ec 28 Summary 6.6.6.6 2.2.2.2 0x8000000a 2807 0x22 0x30e2 28 Summary *7.7.7.7 3.3.3.3 0x8000000b 514 0x22 0xe128 28 Summary 10.26.26.0 2.2.2.2 0x80000050 407 0x22 0xddc8 28 Summary *10.37.37.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000031 787 0x22 0xffab 28 Summary 10.45.45.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000048 272 0x22 0xfa85 28 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.3 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router *3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x80000010 1333 0x20 0x4d0b 36 Router 7.7.7.7 7.7.7.7 0x80000016 2242 0x20 0xf40e 48 Network 10.37.37.7 7.7.7.7 0x80000009 1814 0x20 0x4153 32 NSSA *0.0.0.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000005 1605 0x20 0x8197 36 |
nah, sperti yang anda lihat net 0.0.0.0/0 sebgaia NSSA.
coba anda tambahkan dummy static pada R7 sperti berikut:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
set routing-options static route 172.16.2.0/24 discard set routing-options static route 172.16.3.0/24 discard set routing-options static route 172.16.4.0/24 discard set routing-options static route 172.16.0.0/24 discard set routing-options static route 172.16.1.0/24 discard |
coba lakukan show ospf database pada R3.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
root@JuniperX# run show ospf database logical-system r3 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.0 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 0x800000c1 1761 0x22 0xd37d 72 Router 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x8000008f 2362 0x22 0x2c07 48 Router *3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x8000007a 2306 0x22 0xa48f 48 Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000081 1094 0x22 0xed13 60 Network 10.12.12.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000038 1763 0x22 0xbf0b 32 Network *10.13.13.3 3.3.3.3 0x8000003d 2033 0x22 0x9822 32 Network 10.14.14.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000048 1260 0x22 0x653f 32 Summary 5.5.5.5 4.4.4.4 0x8000000a 1760 0x22 0x22ec 28 Summary 6.6.6.6 2.2.2.2 0x8000000a 2962 0x22 0x30e2 28 Summary *7.7.7.7 3.3.3.3 0x8000000b 669 0x22 0xe128 28 Summary 10.26.26.0 2.2.2.2 0x80000050 562 0x22 0xddc8 28 Summary *10.37.37.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000031 942 0x22 0xffab 28 Summary 10.45.45.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000048 427 0x22 0xfa85 28 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.3 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router *3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x80000010 1488 0x20 0x4d0b 36 Router 7.7.7.7 7.7.7.7 0x80000016 2397 0x20 0xf40e 48 Network 10.37.37.7 7.7.7.7 0x80000009 1969 0x20 0x4153 32 NSSA *0.0.0.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000005 1760 0x20 0x8197 36 NSSA 172.16.0.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000006 1112 0x28 0x8729 36 NSSA 172.16.1.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000005 1540 0x28 0x7e32 36 NSSA 172.16.2.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000006 683 0x28 0x713d 36 NSSA 172.16.3.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000006 255 0x28 0x6647 36 NSSA 172.16.4.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000005 2826 0x28 0x5d50 36 OSPF AS SCOPE link state database Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Extern *172.16.0.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000007 397 0x22 0x7453 36 Extern *172.16.1.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000007 124 0x22 0x695d 36 Extern *172.16.2.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000006 2851 0x22 0x6066 36 Extern *172.16.3.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000006 2578 0x22 0x5570 36 Extern *172.16.4.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000005 1215 0x22 0x4c79 36 |
nah, net 172.x.x.x sudah adjacent juga pada R3. skrng cek pada R7.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
root@JuniperX# run show ospf database logical-system r7 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.3 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x80000010 1664 0x20 0x4d0b 36 Router *7.7.7.7 7.7.7.7 0x80000016 2571 0x20 0xf40e 48 Network *10.37.37.7 7.7.7.7 0x80000009 2143 0x20 0x4153 32 NSSA 0.0.0.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000005 1936 0x20 0x8197 36 NSSA *172.16.0.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000006 1286 0x28 0x8729 36 NSSA *172.16.1.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000005 1714 0x28 0x7e32 36 NSSA *172.16.2.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000006 857 0x28 0x713d 36 NSSA *172.16.3.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000006 429 0x28 0x6647 36 NSSA *172.16.4.0 7.7.7.7 0x80000005 3000 0x28 0x5d50 36 |
Pertannyaanya apakah R7 bisa reach ke area lain misal R6 atau R5, tentu bisa karena pada database ospf dengan LSA type 7 NSSA net 0.0.0.0. mari kita cek dengan traceroute dari R7.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
root@JuniperX# run traceroute 6.6.6.6 logical-system r7 traceroute to 6.6.6.6 (6.6.6.6), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.37.37.3 (10.37.37.3) 0.179 ms 0.140 ms 0.106 ms 2 10.13.13.1 (10.13.13.1) 0.207 ms 0.358 ms 0.248 ms 3 10.12.12.2 (10.12.12.2) 0.305 ms 0.329 ms 0.352 ms 4 6.6.6.6 (6.6.6.6) 0.387 ms 0.594 ms 0.467 ms [edit] root@JuniperX# run traceroute 5.5.5.5 logical-system r7 traceroute to 5.5.5.5 (5.5.5.5), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 10.37.37.3 (10.37.37.3) 0.172 ms 0.177 ms 0.122 ms 2 10.13.13.1 (10.13.13.1) 0.220 ms 0.211 ms 0.197 ms 3 10.14.14.4 (10.14.14.4) 0.348 ms 0.339 ms 0.306 ms 4 5.5.5.5 (5.5.5.5) 0.393 ms 0.399 ms 0.392 ms |
mari kita lihat bagaimana LSA type untuk route under area nssa router, bila dari sisi area lain, sebgai contoh R5.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
root@JuniperX# run show ospf database logical-system r5 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.1 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000081 1082 0x22 0x457a 36 Router *5.5.5.5 5.5.5.5 0x8000006c 2254 0x22 0x396f 48 Network *10.45.45.5 5.5.5.5 0x80000014 2254 0x22 0x92f2 32 Summary 1.1.1.1 4.4.4.4 0x80000007 1415 0x22 0xe041 28 Summary 2.2.2.2 4.4.4.4 0x80000007 748 0x22 0xbc60 28 Summary 3.3.3.3 4.4.4.4 0x80000007 82 0x22 0x8e8a 28 Summary 4.4.4.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000014 1915 0x22 0x5ab3 28 Summary 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000013 2082 0x22 0x34d6 28 Summary 6.6.6.6 4.4.4.4 0x80000006 582 0x22 0x10fc 28 Summary 7.7.7.7 4.4.4.4 0x80000005 2915 0x22 0xe326 28 Summary 10.12.12.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000007 415 0x22 0x8181 28 Summary 10.13.13.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000006 2748 0x22 0x6c95 28 Summary 10.14.14.0 4.4.4.4 0x8000004d 1248 0x22 0xbcfc 28 Summary 10.26.26.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000006 248 0x22 0x4a9c 28 Summary 10.37.37.0 4.4.4.4 0x80000005 2582 0x22 0x4e83 28 ASBRSum 3.3.3.3 4.4.4.4 0x80000005 2415 0x22 0x8495 28 OSPF AS SCOPE link state database Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Extern 172.16.0.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000007 889 0x22 0x7453 36 Extern 172.16.1.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000007 616 0x22 0x695d 36 Extern 172.16.2.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000007 343 0x22 0x5e67 36 Extern 172.16.3.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000007 70 0x22 0x5371 36 Extern 172.16.4.0 3.3.3.3 0x80000005 1707 0x22 0x4c79 36 |
yess, anda bisa lihat sperti diats, bahwa network 172.x.x.x dikenal sbegai LSA type 5, kenapa demikian? karena ini merepesentasikan network tersebut di redistibute dari routing protokol lain dalam hal ini static route.
oke cukup yee..smoga bermanfaat 🙂
good luck!
[Junos Routing] Redistribute Static ke OSPF
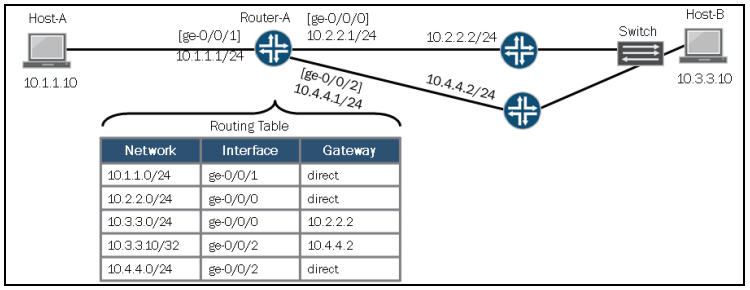
Mari kita lanjutkan, masih seputar ospf. Kali ini ane mau share, dari gambar tulisan ini , R1 ke R-ISP itu menggunakan static route tepatnya di config kali ini menggunakan default route. Nah protokol ospf dan routing static tidak langsung bsa tukar informasi routing, supaya bisa tukar informasi routing, kita perlu redistribute protokol static ke dalam ospf. Ini anda hanya perlu fokus pada R1 dan R-ISP untuk confignya,…
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
R-ISP set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 10 vlan-id 10 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 10 family inet address 10.10.10.10/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 10 family inet address 100.100.100.1/32 set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.10.10.1 R1 Create policy: set policy-options policy-statement <strong>export_static</strong> term 1 from protocol <strong>static</strong> set policy-options policy-statement <strong>export_static</strong> term 1 then <strong>accept</strong> create static route: set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 10.10.10.10 export to protocol ospf: set protocols ospf export <strong>export_static </strong> |
Nah, kira2 ada gambaran ya,,jadi klo soal redistribute anda cukup masuk di hararki policy-options, jadi dah, hehe. Sekarang mari kita lihat hasilnya.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
root@vMX-1> show route logical-system r-isp inet.0: 4 destinations, 4 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 0.0.0.0/0 *[Static/5] 00:07:01 > to 10.10.10.1 via ge-0/0/0.10 10.10.10.0/24 *[Direct/0] 08:28:09 > via ge-0/0/0.10 10.10.10.10/32 *[Local/0] 08:28:20 Local via ge-0/0/0.10 100.100.100.1/32 *[Direct/0] 08:29:06 > via lo0.10 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
root@vMX-1> show route logical-system r4 inet.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both <strong>0.0.0.0/0 *[OSPF/150] 00:07:54, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34</strong> 1.1.1.1/32 *[OSPF/150] 08:14:42, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34 2.2.2.2/32 *[OSPF/150] 08:14:42, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 3.3.3.3/32 *[OSPF/150] 08:14:42, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34 4.4.4.4/32 *[Direct/0] 08:29:59 > via lo0.4 10.10.10.0/24 *[OSPF/150] 08:14:42, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34 10.12.12.0/24 *[OSPF/10] 08:28:12, metric 2 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 10.13.13.0/24 *[OSPF/10] 08:28:12, metric 2 > to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34 ---(more)---[abort] |
Coba lihat di show route R4, ada network 0.0.0.0/0, ini artinya routing static yang tadi kita create di R1 berhasil di redistribute ke ospf. jadi selain R1 yaitu R2, R3, R4 0.0.0.0/0 dikenal sebagai network ospf. coba lakukan test ping seperti berikut:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
root@vMX-1> ping 100.100.100.1 logical-system r3 PING 100.100.100.1 (100.100.100.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 100.100.100.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=3.021 ms 64 bytes from 100.100.100.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=9.659 ms 64 bytes from 100.100.100.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=4.244 ms ^C --- 100.100.100.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 3.021/5.641/9.659/2.884 ms root@vMX-1> ping 100.100.100.1 logical-system r2 PING 100.100.100.1 (100.100.100.1): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 100.100.100.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time=3.387 ms 64 bytes from 100.100.100.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=3.629 ms ^C --- 100.100.100.1 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 3.387/3.508/3.629/0.121 ms |
Ok Good Luck! 🙂
[Junos Routing] Redistribute Protokol Direct ke OPSF
Ini hanya mau menyambung tulisan ane sbelumnya yang ada di blog ini, klo mau cek dsini, jadi kira2 tau kan apa yang akan kita bahas,? klo omongin maslah redistribute itu adalah ada istilah cisco, jadi ane pinjam dlu ye,,,biar familiar gtu,,,klo di junos istilahnya routing policy. Oke kita review kembali tulisan seblumnya bahwa semua interface yang ada di router ospf, kita masukin semua ke protokol ospf, nah kli ini tidak demikian, kita hanya perlu memasukkan interface p2p router ospf, misal anda memiliki interface local area network, interface loopbak or alias interface yang base L3 nya di router bisa kita lakukan advertise via protokol direct dengan meredistribute ke ospf, atau dalam junos bisa kita export ke protokol ospf. Jadi secara praktisnya, jika anda menambah l3 di router anda, maka akan secara otomatis ke advertise ke ospf interface tersebut. Untuk lebih jelasnya mari kita lihat step berikut,.
Cek protokol direct di junos.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
root@vMX-1> show route protocol direct logical-system r1 inet.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (13 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 1.1.1.1/32 *[Direct/0] 00:02:10 > via lo0.1 10.10.10.0/24 *[Direct/0] 00:01:13 > via ge-0/0/1.10 10.12.12.0/24 *[Direct/0] 00:01:13 > via ge-0/0/1.12 10.13.13.0/24 *[Direct/0] 00:01:13 > via ge-0/0/1.13 |
nah, coba lihat network direct 🙂 di R1 nya,..hehe..nah R1 agar bisa ngobrol dengan R2 dan R3 apa yang perlu anda lakukan? anda hanya perlu kasih tau potokol ospf nya interface mana yang konek ke router tersebut,. terus interface yang misal ada interface buat lan, atau yang ke network data center, perlu di advertise ke ospf gk? pada tulisan kali ini anda tidak perlu melakukannya, karena anda hanya cukup export protkol direct ini ke ospf., nah berikut yang harus anda lakukan pertama adalah membuat policy baru dengan untuk protokol direct seperti berikut:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
R1: set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 then accept R2: set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 then accept R3: set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 then accept R4: set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement export_direct term 1 then accept |
Nah anda tinggal export policy nya ke dalam ospf atau di cisco itu di redistribute ke ospf.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
R1: set protocols ospf export export_direct set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.12 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.13 R2: set protocols ospf export export_direct set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.12 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.24 R3: set protocols ospf export export_direct set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/3.13 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/3.34 R4: set protocols ospf export export_direct set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/4.24 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/4.34 |
Pada konfigurasi di atas, anda cukup advertise interface yang koneksi antar router, bila router tersebut menggunakan ospf. skrang mari kita cek hasilnya,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
root@vMX-1# run show route protocol ospf logical-system r2 inet.0: 12 destinations, 12 routes (12 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 1.1.1.1/32 *[OSPF/150] 00:09:02, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.12.12.1 via ge-0/0/2.12 3.3.3.3/32 *[OSPF/150] 00:09:02, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.12.12.1 via ge-0/0/2.12 to 10.24.24.4 via ge-0/0/2.24 4.4.4.4/32 *[OSPF/150] 00:09:02, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.24.24.4 via ge-0/0/2.24 10.10.10.0/24 *[OSPF/150] 00:09:02, metric 0, tag 0 > to 10.12.12.1 via ge-0/0/2.12 10.13.13.0/24 *[OSPF/10] 00:22:21, metric 2 > to 10.12.12.1 via ge-0/0/2.12 10.34.34.0/24 *[OSPF/10] 00:22:32, metric 2 > to 10.24.24.4 via ge-0/0/2.24 224.0.0.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:24:28, metric 1 MultiRecv |
Nah, bisa anda cek di table route ditas, bahwa interface loopback yang ada dimasing2 router, ke advertise juga ke ospf.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
root@vMX-1# run show ospf database logical-system r2 OSPF database, Area 0.0.0.0 Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 0x80000007 653 0x22 0x750a 48 Router *2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000007 652 0x22 0x49fe 48 Router 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x80000007 654 0x22 0xe030 48 Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000006 653 0x22 0x9842 48 Network *10.12.12.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000001 1458 0x22 0x2ed3 32 Network 10.13.13.3 3.3.3.3 0x80000001 1465 0x22 0x11e5 32 Network 10.24.24.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000002 342 0x22 0x3d95 32 Network 10.34.34.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000001 1469 0x22 0x8a31 32 OSPF AS SCOPE link state database Type ID Adv Rtr Seq Age Opt Cksum Len Extern 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 0x80000001 653 0x22 0xb4f5 36 Extern *2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 0x80000001 652 0x22 0x683a 36 Extern 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 0x80000001 654 0x22 0x1c7e 36 Extern 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 0x80000001 653 0x22 0xcfc2 36 Extern 10.10.10.0 1.1.1.1 0x80000001 653 0x22 0x7917 36 |
Karena modelnya di redistribute, jadi ospf mengenalnya sebgai Extern (external lsa type)
Ok Good Lucy guys…, 🙂
[Junos Routing] Basic Routing OSPF
Semangat mengisi blog ini :), kesempatan kali ini ane mau share konfigurasi dasar routing ospf di juniper. Untuk membuat router juniper agar dapat saling komunikasi menggunakan protokol ospf, anda hanya perlu advertise semua interface tersebut ke dalam protokol ospf. secara dynamic protokol ospf akan segera aktif alias akan menemuakan router tetangga yang tentu menggunakan protokol ospf juga. nah berikut tak kasih gambat biar sedikit ada gambaran hehe…
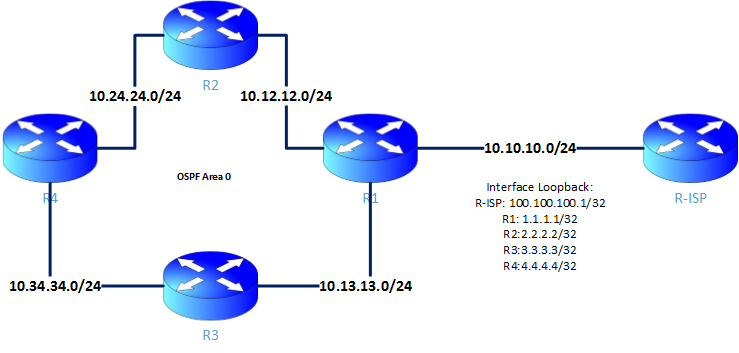 Untuk tulisan ini, anda hanya perlu fokus pada R1,R2, R3 dan R4. Karena R1 ke arah R-ISP akan dibahas secara terpisah, so kapan dibhas,? silahkan tunggu ja ya haha.. Oke mari kita mulai dengan konfigurasi interface, ohy lab ini pastikan anda sudah mengerti cara create logical router atau logical systems.
Untuk tulisan ini, anda hanya perlu fokus pada R1,R2, R3 dan R4. Karena R1 ke arah R-ISP akan dibahas secara terpisah, so kapan dibhas,? silahkan tunggu ja ya haha.. Oke mari kita mulai dengan konfigurasi interface, ohy lab ini pastikan anda sudah mengerti cara create logical router atau logical systems.
Step 01 : Konfigurasi Interface
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 10 vlan-id 10 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 10 family inet address 10.10.10.1/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 12 vlan-id 12 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 12 family inet address 10.12.12.1/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 13 vlan-id 13 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 13 family inet address 10.13.13.1/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 1.1.1.1/32 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 12 vlan-id 12 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 12 family inet address 10.12.12.2/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 24 vlan-id 24 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 24 family inet address 10.24.24.2/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 2.2.2.2/32 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 13 vlan-id 13 set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 13 family inet address 10.13.13.3/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 34 vlan-id 34 set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 34 family inet address 10.34.34.3/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 3.3.3.3/32 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 24 vlan-id 24 set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 24 family inet address 10.24.24.4/24 set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 34 vlan-id 34 set interfaces ge-0/0/4 unit 34 family inet address 10.34.34.4/24 set interfaces lo0 unit 4 family inet address 4.4.4.4/32 |
Step02 : Konfigurasi protokol OSPF
Seperti yang ane sampaikan di awal, by default ospf akan langsung melakukan update bila anda sudah advertise interface lokal di rouer tersebut, penasaran lanjut klo bgtu,,,:)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
R1 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.12 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.13 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.1 R2 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.12 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.24 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.2 R3 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/3.13 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/3.34 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.3 R4 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/4.24 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/4.34 set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.4 |
Step03: Verifikasi and Testing
It’s time to check, hehe…pertama anda bisa melakukan cek routing, sperti berikut:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
[edit] root@vMX-1# run show route logical-system r4 inet.0: 11 destinations, 11 routes (11 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 1.1.1.1/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:21:50, metric 2 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34 2.2.2.2/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:22:05, metric 1 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 3.3.3.3/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:22:00, metric 1 > to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34 4.4.4.4/32 *[Direct/0] 00:33:15 > via lo0.4 10.12.12.0/24 *[OSPF/10] 00:22:05, metric 2 > to 10.24.24.2 via ge-0/0/4.24 10.13.13.0/24 *[OSPF/10] 00:22:00, metric 2 > to 10.34.34.3 via ge-0/0/4.34 10.24.24.0/24 *[Direct/0] 00:33:15 > via ge-0/0/4.24 10.24.24.4/32 *[Local/0] 00:33:15 Local via ge-0/0/4.24 10.34.34.0/24 *[Direct/0] 00:33:15 > via ge-0/0/4.34 10.34.34.4/32 *[Local/0] 00:33:15 Local via ge-0/0/4.34 224.0.0.5/32 *[OSPF/10] 00:22:55, metric 1 MultiRecv |
Coba test ping seperti berikut:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
root@vMX-1# run ping 1.1.1.1 logical-system r4 rapid PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1): 56 data bytes !!!!! --- 1.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 2.368/2.763/3.174/0.339 ms [edit] root@vMX-1# run ping 1.1.1.1 logical-system r2 rapid PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1): 56 data bytes !!!!! --- 1.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.444/1.680/2.286/0.317 ms [edit] root@vMX-1# run ping 1.1.1.1 logical-system r3 rapid PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1): 56 data bytes !!!!! --- 1.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.452/1.664/2.028/0.202 ms |
Good Luck!
[Junos Routing] Cara Konfigurasi Routing RIP
Yeahhh…udah lama gk nulis, hehe…ini ane baru nulis lagi di blog routecloud,. oke kali ini mau ngebahas cara konekin router juniper menggunakan routing protokol rip, nah mari kita lihat gambar berikut ini supaya lebih jelas 🙂
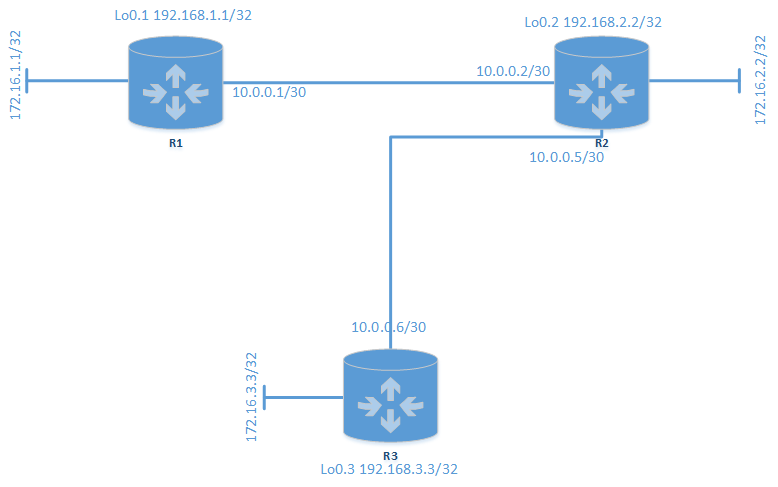 Siippp..gambar sudah ada,,jadi tinggal config dah..
Siippp..gambar sudah ada,,jadi tinggal config dah..
#01 Config IP di R1, R2, R3
R1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 12 vlan-id 12 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 12 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 vlan-id 1 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 1 family inet address 192.168.1.1/32 |
R2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 vlan-id 2 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 2 family inet address 172.16.2.2/32 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 12 vlan-id 12 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 12 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 23 vlan-id 23 set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 23 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces lo0 unit 2 family inet address 192.168.2.2/32 |
R3:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 23 vlan-id 23 set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 23 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 3 vlan-id 3 set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 3 family inet address 192.168.3.3/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 3 family inet address 172.16.3.3/32 |
#02 Setting Routing RIP
R1:
|
1 2 3 |
set protocols rip import rip-import set protocols rip group rip-group export advertise-rip set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor ge-0/0/0.12 |
R2:
|
1 2 3 |
set protocols rip group rip-group export advertise-rip set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor ge-0/0/2.12 set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor ge-0/0/2.23 |
R3:
|
1 2 |
set protocols rip group rip-group export advertise-rip set protocols rip group rip-group neighbor ge-0/0/0.23 |
#03 Konfigurasi Policy untuk meng-advertise protocol direct dan rip,
R1:
|
1 2 3 |
set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 from protocol rip set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 then accept |
R2:
|
1 2 3 |
set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 from protocol rip set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 then accept |
R3:
|
1 2 3 |
set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 from protocol direct set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 from protocol rip set policy-options policy-statement advertise-rip term 1 then accept |
#04 Klo sudah selsai jangan lupa di commit, saatnya anda melakukan test, apakah R1, R2, R3 sudah saling tukar routing information? mari kita cek dengan show route.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
root@R3# run show route protocol rip inet.0: 10 destinations, 11 routes (10 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both 10.0.0.0/30 *[RIP/100] 01:09:22, metric 2, tag 0 > to 10.0.0.5 via ge-0/0/0.23 172.16.0.1/32 *[RIP/100] 01:09:22, metric 3, tag 0 > to 10.0.0.5 via ge-0/0/0.23 172.16.2.2/32 *[RIP/100] 01:09:22, metric 2, tag 0 > to 10.0.0.5 via ge-0/0/0.23 192.168.1.1/32 *[RIP/100] 01:09:22, metric 3, tag 0 > to 10.0.0.5 via ge-0/0/0.23 192.168.2.2/32 *[RIP/100] 01:09:22, metric 2, tag 0 > to 10.0.0.5 via ge-0/0/0.23 224.0.0.9/32 *[RIP/100] 01:09:22, metric 1 MultiRecv |
nahh,,di R3 sudah dapat route ke 172.16.0.1 yang mana itu adalah ip R1, sory ye klo di gambar ip nya 172.16.1.1 hehe.. selanjutnya mari kita coba test ping
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
root@vMX-1# run ping 172.16.0.1 logical-system R3 rapid PING 172.16.0.1 (172.16.0.1): 56 data bytes !!!!! --- 172.16.0.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.808/2.516/3.537/0.645 ms [edit logical-systems R1] root@vMX-1# run ping 172.16.0.1 logical-system R2 rapid PING 172.16.0.1 (172.16.0.1): 56 data bytes !!!!! --- 172.16.0.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.307/1.414/1.606/0.112 ms [edit logical-systems R1] root@vMX-1# run ping 172.16.0.1 logical-system R1 rapid PING 172.16.0.1 (172.16.0.1): 56 data bytes !!!!! --- 172.16.0.1 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 0.014/0.022/0.038/0.008 ms |
Sekian ya,, semoga membantu 🙂
Komentar