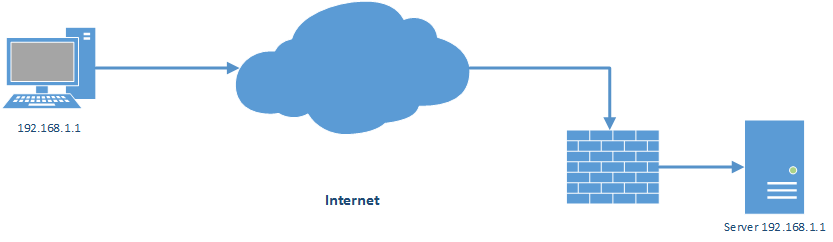
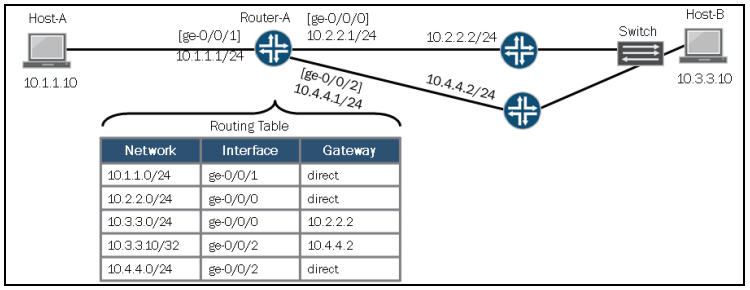
Ini adalah artikel nat pertama sebagai fondasi untuk memahami artikel tentang nat selanjutnya. karena ane berencana membahas nat secara keseluruhan yang dibutuhkan di real network or most real scenario terutama yang menggunankan platform juniper srx 🙂 As general description bahwa fungsi NAT atau network address translation untuk mentranslasikan public address ke private address, atau boleh dikatakan juga menstranslasikan dari alamat satu ke alamat ip yang lain nya. Supaya lebih jelas mari kita lihat gambar berikut:
Category: Network and Security
Apa itu OpenLiteSpeed ?
OpenLiteSpeed adalah web server yang dikembangan oleh LiteSpeed Technologies, Inc. yang memiliki banyak fitur jika dibandingkan dengan web server yang lainnya seperti nginx atau apache. diantaranya adalah open source, free, high performence dan lightweight HTTP dengan mengunakan web user interface administrator.
Fitur Utama
- Arsitektur Event Driven dengan sumber daya yang rendah pada (RAM dan CPU) dari pengunaan yang berlebihan.
- Menangani ratusan ribu koneksi secara bersamaan tanpa mengalami lonjakan yang berlebihan
- GUI Web Admin dengan statistik secata real time
- Rewrite Engine mengunakan sintax apache mod_rewrite
- Dapat melakukan wroker process untuk scalability web. dengan memiliki kemampuan untuk melakukan pekerjaan tertentu pada wroker tertentu.
- High Performance coding mengunakan kqueue (FreeBSD dan OS X), epoll (Linux), /dev/poll (Solaris), dan poll
- High Performance untuk caching halaman web
- Support untuk modul third party melalui API (Application Programming Interface) seperti LSIAPI
- Lihat Lebih lengkap disini
MPLS Concepts and Components
Sebuah router yang mengaktifkan fitur Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) akan memforwad traffic berdasarkan label yang disisipkan pada header packet. Kenapa disebut multiprotocol karena MPLS dapat digunakan untuk memforward berbagai macam tipe paket melalui semua Network protocol layer 2 menggunakan teknik sederhana switching. Secara sederhana topologi service provider yang enable MPLS terdiri dari CE (Customer Edge) router, PE (Provider Edge) router dan P (Provider Core) router. Read More
Network Telco Engineer – SDN/NFV Enthusiast
[Junos Security] Semua tentang si Zones
judulnya itu loh hoho….jadi ini artikel ingin membahas semua tentang si zones tapi bukan bang jones yang jauh disana yak hahaha :P. Semoga tulisan ini memberikan pengertian yang mendalam terkait apa itu zone pada juniper SRX? berikut ane kutip dari juniper.net;
A zone is a collection of one or more network segments sharing identical security requirements. To group network segments within a zone, you must assign logical interfaces from the device to a zone.
Jadi zone bisa disebut sebagai sebuah atau sekumpulan dari segment network yang memiliki ketentuan atau requerement yang sama. Sebagai contoh anda memiliki beberapa server maka anda mengelompokkan ke dalam zone Server atau DMZ, terus user-user yang akan menggunakan layanan server anda tentu berbeda dengan server yang anda miliki, dan anda mempertimbangkan tidak ingin server anda menyatu dengan jaringan user2, maka anda bisa memisahkan dengan zone User misalnya, dan seterusnya.. Jadi zone ini berfungsi memisahkan network yang ingin anda proteksi dari segmen network lain. Jika anda berpikir, bagaimana cara melakukannya? Silahkan ikutti langkah berikut:
- Define zone (security or functional)
- Add logical interfaces to the zone
- Define permitted services (example: Telnet, SSH) and protocols (example: OSPF) destined to device itself.
So,,. anda sudah tahu apa yang harus anda lakukan? Jadi diatas setidaknya ada tiga langkah ya untuk membuat zone, untuk zone itu sendiri ada security zone yaitu zone yang memang untuk mengidentifikasi flow traffic, sedangkan functional zone adalah zone khusus management srx, misal untuk remote srx anda bisa melakukan via interface yang di set sebagai functional atau management zone. Selanjutnya di dalam zone anda perlu menambahkan interface yang dari awal sudah anda identifikasi. Misal interface yang terkoneksi dengan server2, anda bisa memasukkan ke zone DMZ yang sudah anda buat. Langkah selanjutnya adalah mendefinisikan permit service seperti ssh, ping, atau ospf. Service ini bukan untuk mempermit traffic dari zone satu ke zone yang lain, akan tetapi service yang diizinkan dari host2 zone terkait ke interface SRX itu sendiri.
Oke, mari kita lihat detail satu persatu di SRX.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
root# set security zones ? Possible completions: + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups > functional-zone Functional zone > security-zone Security zones [edit] |
jadi zone ada dua ya functional-zone, coba kita cek opsi selanjutnya.
|
1 2 3 4 |
root# set security zones functional-zone ? Possible completions: > management Host for out of band management interfaces [edit] |
nama zone sudah di define ya yaitu management zone,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
root# set security zones functional-zone management ? Possible completions: <[Enter]> Execute this command + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups description Text description of zone > host-inbound-traffic Allowed system services & protocols > interfaces Interfaces that are part of this zone screen Name of ids option object applied to the zone | Pipe through a command [edit] |
seperti yang sudah dijelaskan seblumnya, bahwa di zone itu anda perlu menambah logical interface, yaitu di opsi interface, kemudian mempermit traffic yang ke SRX via interface tersebut pada opsi host-inbound-traffic. Mari kita lanjut ke opsi security zone.
|
1 2 3 4 |
root# set security zones security-zone ? Possible completions: <name> Name of the zone [edit] |
oke, coba anda buat security zone baru, misal DMZ.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
root# set security zones security-zone DMZ ? Possible completions: <[Enter]> Execute this command > address-book Address book entries application-tracking Enable Application tracking support for this zone + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups description Text description of zone > host-inbound-traffic Allowed system services & protocols > interfaces Interfaces that are part of this zone screen Name of ids option object applied to the zone tcp-rst Send RST for NON-SYN packet not matching TCP session | Pipe through a command [edit] |
anda perlu menambah interface baru, pilih opsi interface di zone DMZ
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
root# set security zones security-zone DMZ interfaces ? Possible completions: <interface-unit> Logical interface ge-0/0/0 ge-0/0/1 ge-0/0/2 [edit] |
Oke, langkah selanjutnya anda bisa mempermit service di zone DMZ bisa langsung under zone DMZ atau under interface. seperti berikut:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
root# ...rity-zone DMZ interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 host-inbound-traffic ? Possible completions: + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups > protocols Protocol type of incoming traffic to accept > system-services Type of incoming system-service traffic to accept [edit] root# ...rity-zone DMZ interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 host-inbound-traffic |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
root# ...aces ge-0/0/2.0 host-inbound-traffic system-services ? Possible completions: all All system services any-service Enable services on entire port range bootp Bootp and dhcp relay-agent service dhcp Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol dhcpv6 Enable Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 dns DNS service finger Finger service ftp FTP http Web management service using HTTP https Web management service using HTTP secured by SSL ident-reset Send back TCP RST to IDENT request for port 113 ike Internet Key Exchange lsping Label Switched Path ping service netconf NETCONF service ntp Network Time Protocol service ping Internet Control Message Protocol echo requests r2cp Enable Radio-Router Control Protocol service reverse-ssh Reverse SSH service reverse-telnet Reverse telnet service rlogin Rlogin service rpm Real-time performance monitoring rsh Rsh service sip Enable Session Initiation Protocol service snmp Simple Network Management Protocol service snmp-trap Simple Network Management Protocol traps ssh SSH service telnet Telnet service tftp TFTP traceroute Traceroute service xnm-clear-text JUNOScript API for unencrypted traffic over TCP xnm-ssl JUNOScript API service over SSL |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
root# ...aces ge-0/0/2.0 host-inbound-traffic protocols ? Possible completions: all All protocols bfd Bidirectional Forwarding Detection bgp Border Gateway Protocol dvmrp Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol igmp Internet Group Management Protocol ldp Label Distribution Protocol msdp Multicast Source Discovery Protocol nhrp Next Hop Resolution Protocol ospf Open Shortest Path First ospf3 Open Shortest Path First version 3 pgm Pragmatic General Multicast pim Protocol Independent Multicast rip Routing Information Protocol ripng Routing Information Protocol next generation router-discovery Router Discovery rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol sap Session Announcement Protocol vrrp Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol [edit] |
jadi, jika anda menggunakan routing protokol di interface tersebut, maka anda bisa melakukannya di opsi protocol. dan jika anda melakukkannya under interface maka services tersebut hanya berlaku di interface tersebut. jadi jika ada interface yang lain maka itu tidak berlaku. mari kita lihat contoh hasilnya.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
root# show security zones | display set set security zones security-zone DMZ interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 host-inbound-traffic system-services ping set security zones security-zone DMZ interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 host-inbound-traffic system-services dhcp set security zones security-zone DMZ interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 host-inbound-traffic protocols ospf set security zones security-zone DMZ interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 [edit] root# show security zones security-zone DMZ { interfaces { ge-0/0/2.0 { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { ping; dhcp; } protocols { ospf; } } } ge-0/0/1.0; } } [edit] |
nah, bisa anda lihat, contoh di atas, ge-0/0/2.0 memiliki service yang dibolehkan ping, dhcp, dan ospf. sedangkan ge-0/0/1.0 belum ada. Lalu apakah ge-0/0/1.0 sperti ini bermasalah? sebetulnya ini tidak masalah. hanya saja bila interface tersebut disambungkan ke komputer anda, maka anda tidak bisa melakukan apa2 untuk interface tersebut, misal ping, telnet atau lainnya. Oke ada gambaran ya..hehe.. Lalu bagaiamana jika anda melakukannya permit service under zone DMZ
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
root# set security zones security-zone DMZ host-inbound-traffic ? Possible completions: + apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data + apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups > protocols Protocol type of incoming traffic to accept > system-services Type of incoming system-service traffic to accept [edit] |
Contoh hasilnya.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
set security zones security-zone DMZ host-inbound-traffic system-services all set security zones security-zone DMZ host-inbound-traffic protocols all Hasilnya: root# show security zones security-zone DMZ { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { all; } protocols { all; } } interfaces { ge-0/0/2.0 { host-inbound-traffic { system-services { ping; dhcp; } protocols { ospf; } } } ge-0/0/1.0; } } [edit] |
coba anda perhatikan, under zone DMZ di set protocol all system service all. Jika sperti diatas, maka ge-0/0/1.0 service nya all, sedangkan ge-0/0/2.0 tetap seperti yang diset atau yang ane sampaikan sebelumnya.
Untuk melihat hasilnya,silahkan di commit dan coba anda cek di mode operational
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
root> show security zones Security zone: DMZ Send reset for non-SYN session TCP packets: Off Policy configurable: Yes Interfaces bound: 2 Interfaces: ge-0/0/1.0 ge-0/0/2.0 |
lakukan show interface untuk lebih detailnya
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
root> show interfaces ge-0/0/1.0 Logical interface ge-0/0/1.0 (Index 70) (SNMP ifIndex 519) Flags: SNMP-Traps 0x4000 Encapsulation: ENET2 Input packets : 217 Output packets: 109 Security: Zone: DMZ Allowed host-inbound traffic : bootp bfd bgp dns dvmrp igmp ldp msdp nhrp ospf pgm pim rip router-discovery rsvp sap vrrp dhcp finger ftp tftp ident-reset http https ike netconf ping reverse-telnet reverse-ssh rlogin rpm rsh snmp snmp-trap ssh telnet traceroute xnm-clear-text xnm-ssl lsping ntp sip r2cp Protocol inet, MTU: 1500 Flags: Sendbcast-pkt-to-re Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary Destination: 172.31.10/24, Local: 172.31.10.1, Broadcast: 172.31.10.255 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
root> show interfaces ge-0/0/2.0 Logical interface ge-0/0/2.0 (Index 74) (SNMP ifIndex 520) Flags: SNMP-Traps 0x4000 Encapsulation: ENET2 Input packets : 0 Output packets: 1 Security: Zone: DMZ Allowed host-inbound traffic : ospf dhcp ping Protocol inet, MTU: 1500 Flags: Sendbcast-pkt-to-re Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary Destination: 10.0.0/24, Local: 10.0.0.1, Broadcast: 10.0.0.255 |
Oke, ane rasa sudah cukup jelas ya, jika ada pertanyaan silahkan comment dibawah 🙂
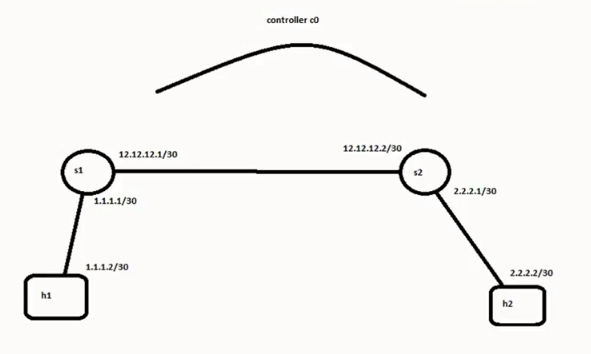
Konfigurasi static routing pada SDN OpenFlow mengunakan Ryu Controller
setelah lama, saya tidak membahas tentang SDN (Software Defined Networking) sekarang saya mau mencoba untuk konfig static route di openflow controller, sebenernya masih banyak yang ingin saya bahas tentang SDN tapi karena banyaknya agenda saya, jadi belum sempat untuk di tulis, hehehe :v
Ryu controller adalah software freamework untuk defined networking, ryu controller mendukung openflow 1.1 – 1.5. ryu dalam bahasa jepang artinya flow
skema topologi yang akan dibuat adalah seperti ini
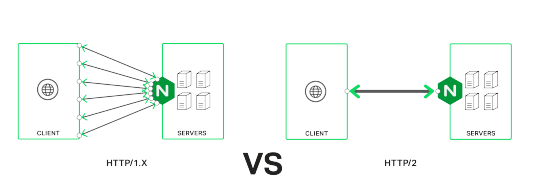
Perbandingan kecepatan http/1.1 vs http/2
Http/2 adalah versi baru dari protocol http, yang mengantikan versi sebelumnya yaitu http/1.1 . http/2 dirilis pada tahun 2015 dan sudah terdaftar pada standar IETF. http/2 sudah mendukung beberapa web server diantaranya adalah nginx. untuk menerapkan http/2 pada website, kita harus mengunakan https.
Install NGINX 1.10, PHP-FPM 7.0, dan MariaDB 10.1 di CentOS 7
Kemarin, saat mengunjungi website NGINX ternyata telah release versi stable yang sudah support untuk HTTP/2. Dimana dengan HTTP/2, website akan di-deliver ke client dengan lebih cepat dibanding dengan HTTP/1.1, bisa dilihat dari link ini https://http2.akamai.com/demo. karena itu admin langsung mau coba deh migrasiin web ini ke HTTP/2. Di tutorial ini yang akan diinstall adalah NGINX versi 1.10, PHP-FPM versi 7.0, dan MariaDB versi 10.1. Let’s get started.
Install NGINX 1.10
pertama yang dilakukan adalah upgrade centos terlebih dahulu
|
1 |
yum -y upgrade |
lalu di-restart jika telah selesai. Read More
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6)
IPv6 dikembangkan pada tahun 1990-an (RFC 2460) yang bertujuan untuk menggantikan IPv4 dengan alasan utama, kapasitas address IPv4 yang sudah mulai habis. IPv6 terdiri dari 128-bit dan dapat menampung total alamat 3.4 × 1038 , sangat jauh berbeda dengan IPv4 yang hanya terdiri dari 32-bit dan hanya dapat menyediakan alamat IP sekitar 4 miliar. Dengan alokasi IP yang sangat besar, dapat dipastikan tidak ada limitasi/pembatasan alamat IP, dengan keadaan seperti ini fleksibilitas dapat dicapai oleh setiap host, terutama perangkat mobile.
IPv6 di definisikan menjadi 3 tipe yang berbeda :
- Unicast : Unicast address digunakan untuk single host
- Multicast : Multicast address digunakan untuk grup hosts
- Anycast : Anycast address digunakan lebih dari satu host, misal ada paket yang ditujukan untuk alamat unicast, maka paket tersebut akan diterima oleh host terdekat ditentukan berdasarkan routing protocol.
Perlu diketahui bahwa IPv6 tidak menyediakan alamat broadcast, muncul pertanyaan”Lalu bagaimana nasib protokol yang memanfaatkan sistem pengalamatan broadcast seperti ARP ?” Read More
Network Telco Engineer – SDN/NFV Enthusiast
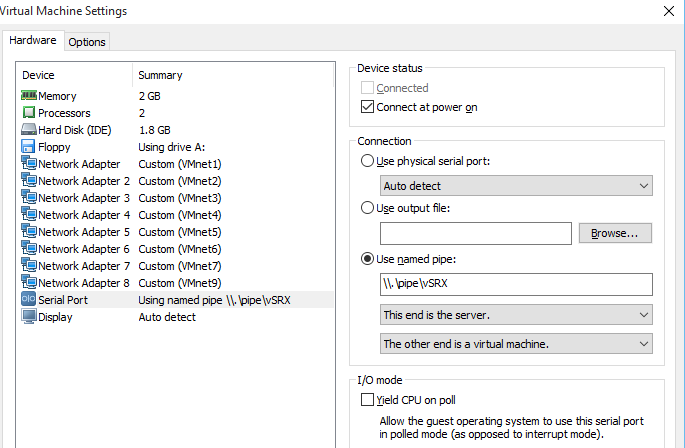
[Junos Security] Bagaimana Mensimulasikan Juniper SRX Pada VMware
Buat anda yang tertarik belajar product security juniper, dalam hal ini adalah SRX. juniper menyediakan tools nya yang dikenal dengan juniper firefly atau juniper vSRX. related juniper secuirty anda bisa membacanya disini. oke anda harus mendownload juniper firefly di junipervsrx (dengan filename;junos-vsrx-12.1X47-D20.7-domestic.ova). Setelah vsrx dam vmware ada di local disk anda. Anda perlu install vmware nya terlebih dahulu setelah itu anda tinggal open file vsrx yang anda download sebulmnya. Silahkan ikuti detail step nya pada tulisan bagaimana memulai belajar juniper. Jika anda mengikuti step nya, minimal coba anda buat kebutuhan interface vsrx seperti tampilan berikut 🙂
[Junos Security] Pengenalan Juniper Security
Hallo pagi semuanya 🙂
Mumpung lagi fresh, masih pagi dan pas banget ini adalah materi awal terkait juniper firewall. Tulisan ini adalah diperuntukkan buat siapa ja yang ingin mengenal product juniper firewall. Yup, tentu anda tau ya pasti apa itu firewall? tembok api bukan? betul, gk tau kenapa perangkat security diistilahkan sbg firewall, klo dalam sejarah2 dunia banyak bangunan atau tembok raksasa yang sengaja dibangun untuk mempertahankan diri dari musuh hehe, sebut saja tembok besar cina, tembok berlin, dan lain-lain. mungkin itu kali ya. Oke jadi product security, semua vendor mengistilahkan sebagai firewall. Nah firewall ini tentu setiap product memiliki feature yang berbeda-beda, tapi fitur2 dasar pasti ada. Klo sebelumnya kita banyak dengar istilah stateless firewall, statefull firewall, traditional firewall, yang baru sekrang istilahnya lagi next generation firewall (NGFW). Sedikit saja mengenai istilah tersebut klo stateless firewall itu kayak access-list di cisco (cisco lagi haha), eh klo di juniper ada juga lah istilahnya firewall filter itu sama dengan cisco, jadi intinya gmn klo stateless? intinya adalah perangkat (biasanya router) hanya menforward paket berdasarkan paket header nya, atau routing table, stateless ini tidak men-track sessionnya itu secara dua arah. misal session saat paket itu berangkat dan saat paket balik lagi. nah klo firewall saat ini sudah statefull, jadi dia akan terus men-track session bolak-baliknya. oke lanjut dulu ya untuk detailnya nanti ane tulisin dibawah hehe. Terus klo traditional firewall bisa kita compare dengan NGFW, jadi traditional firewall memang sudah statefull, tapi content yang dia cek hanya dari IP sampai layer transport dalam hal ini prtokol2 yang termasuk UDP atau TCP, sedangkan NGFW itu sudah mampu melihat atau mengecek atau mengontrol sampe layer aplikasi, baik itu aplikasinya, content, user dan bahkan informasi-informasi yang ada di dalamnya.
Lanjut ya, jadi untuk memahami lebih detail apa yang kita bicarakan diatas, coba kita compare perbedaan router dan firewall.
Komentar